Cherry Picking on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cherry picking, suppressing evidence, or the fallacy of incomplete evidence is the act of pointing to individual cases or data that seem to confirm a particular position while ignoring a significant portion of related and similar cases or data that may contradict that position. Cherry picking may be committed intentionally or unintentionally.
The term is based on the perceived process of harvesting fruit, such as cherries. The picker would be expected to select only the ripest and healthiest fruits. An observer who sees only the selected fruit may thus wrongly conclude that most, or even all, of the tree's fruit is in a likewise good condition. This can also give a false impression of the quality of the fruit (since it is only a sample and is not a representative sample). A concept sometimes confused with cherry picking is the idea of gathering only the fruit that is easy to harvest, while ignoring other fruit that is higher up on the tree and thus more difficult to obtain (see low-hanging fruit).
Cherry picking has a negative connotation as the practice neglects, overlooks or directly suppresses evidence that could lead to a complete picture.
Cherry picking can be found in many
Cherry picking, suppressing evidence, or the fallacy of incomplete evidence is the act of pointing to individual cases or data that seem to confirm a particular position while ignoring a significant portion of related and similar cases or data that may contradict that position. Cherry picking may be committed intentionally or unintentionally.
The term is based on the perceived process of harvesting fruit, such as cherries. The picker would be expected to select only the ripest and healthiest fruits. An observer who sees only the selected fruit may thus wrongly conclude that most, or even all, of the tree's fruit is in a likewise good condition. This can also give a false impression of the quality of the fruit (since it is only a sample and is not a representative sample). A concept sometimes confused with cherry picking is the idea of gathering only the fruit that is easy to harvest, while ignoring other fruit that is higher up on the tree and thus more difficult to obtain (see low-hanging fruit).
Cherry picking has a negative connotation as the practice neglects, overlooks or directly suppresses evidence that could lead to a complete picture.
Cherry picking can be found in many
 Cherry picking, suppressing evidence, or the fallacy of incomplete evidence is the act of pointing to individual cases or data that seem to confirm a particular position while ignoring a significant portion of related and similar cases or data that may contradict that position. Cherry picking may be committed intentionally or unintentionally.
The term is based on the perceived process of harvesting fruit, such as cherries. The picker would be expected to select only the ripest and healthiest fruits. An observer who sees only the selected fruit may thus wrongly conclude that most, or even all, of the tree's fruit is in a likewise good condition. This can also give a false impression of the quality of the fruit (since it is only a sample and is not a representative sample). A concept sometimes confused with cherry picking is the idea of gathering only the fruit that is easy to harvest, while ignoring other fruit that is higher up on the tree and thus more difficult to obtain (see low-hanging fruit).
Cherry picking has a negative connotation as the practice neglects, overlooks or directly suppresses evidence that could lead to a complete picture.
Cherry picking can be found in many
Cherry picking, suppressing evidence, or the fallacy of incomplete evidence is the act of pointing to individual cases or data that seem to confirm a particular position while ignoring a significant portion of related and similar cases or data that may contradict that position. Cherry picking may be committed intentionally or unintentionally.
The term is based on the perceived process of harvesting fruit, such as cherries. The picker would be expected to select only the ripest and healthiest fruits. An observer who sees only the selected fruit may thus wrongly conclude that most, or even all, of the tree's fruit is in a likewise good condition. This can also give a false impression of the quality of the fruit (since it is only a sample and is not a representative sample). A concept sometimes confused with cherry picking is the idea of gathering only the fruit that is easy to harvest, while ignoring other fruit that is higher up on the tree and thus more difficult to obtain (see low-hanging fruit).
Cherry picking has a negative connotation as the practice neglects, overlooks or directly suppresses evidence that could lead to a complete picture.
Cherry picking can be found in many logical fallacies In philosophy, a formal fallacy, deductive fallacy, logical fallacy or non sequitur (; Latin for " tdoes not follow") is a pattern of reasoning rendered invalid by a flaw in its logical structure that can neatly be expressed in a standard logic syst ...
. For example, the "fallacy of anecdotal evidence" tends to overlook large amounts of data in favor of that known personally, "selective use of evidence" rejects material unfavorable to an argument, while a false dichotomy
A false dilemma, also referred to as false dichotomy or false binary, is an informal fallacy based on a premise that erroneously limits what options are available. The source of the fallacy lies not in an invalid form of inference but in a false ...
picks only two options when more are available. Some scholars classify cherry-picking as a fallacy
A fallacy is the use of invalid or otherwise faulty reasoning, or "wrong moves," in the construction of an argument which may appear stronger than it really is if the fallacy is not spotted. The term in the Western intellectual tradition was intr ...
of selective attention, the most common example of which is the confirmation bias
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values. People display this bias when they select information that supports their views, ignoring ...
. Cherry picking can refer to the selection of data or data sets so a study or survey will give desired, predictable results which may be misleading or even completely contrary to reality.
History
An anecdotal story about the 5th centuryBCE
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
atheist philosopher Diagoras of Melos
Diagoras "the Atheist" of Melos ( el, Διαγόρας ὁ Μήλιος) was a Greek poet and sophist of the 5th century BC. Throughout antiquity, he was regarded as an atheist, but very little is known for certain about what he actually believed. ...
says how, when shown the votive gifts of people who had supposedly escaped death by shipwreck by praying to gods, he pointed out that many people ''had'' died at sea in spite of their prayers, yet these cases were not likewise commemorated. Michel de Montaigne
Michel Eyquem, Sieur de Montaigne ( ; ; 28 February 1533 – 13 September 1592), also known as the Lord of Montaigne, was one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance. He is known for popularizing the essay as a liter ...
(1533–1592) in his Essays (Montaigne), essay on prophecies comments on people willing to believe in the validity of supposed seers:
In science
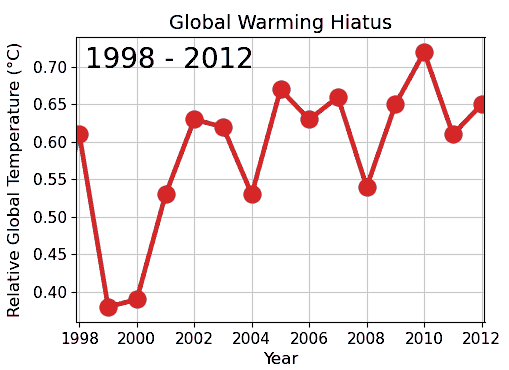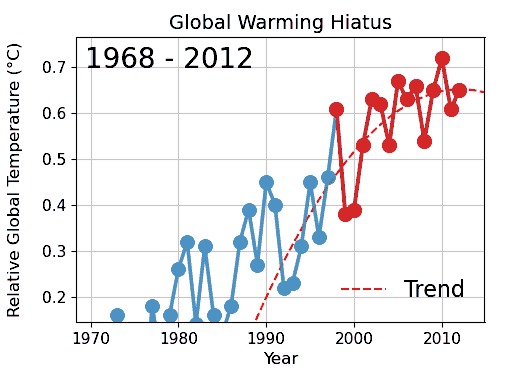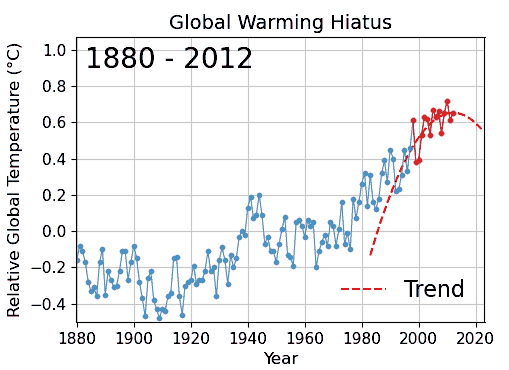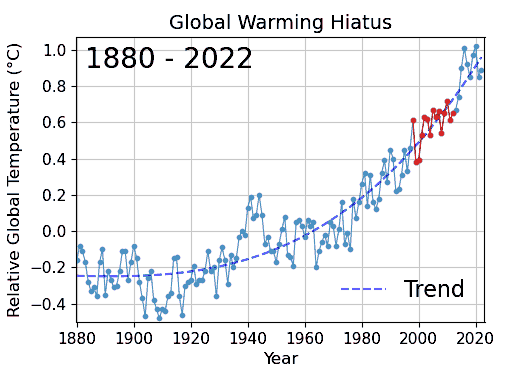
Cherry picking is one of the epistemological characteristics of denialism and widely used by different science Denialism, denialists to seemingly contradict scientific findings. For example, it is used in climate change denial, evolution denial by creationists, denial of the negative health effects of consuming Health effects of tobacco, tobacco products and passive smoking.In medicine
In a 2002 study, a review of previous medical data found cherry picking in tests of anti-depression medication:[researchers] reviewed 31 antidepressant efficacy trials to identify the primary exclusion criteria used in determining eligibility for participation. Their findings suggest that patients in current antidepressant trials represent only a minority of patients treated in routine clinical practice for depression. Excluding potential clinical trial subjects with certain profiles means that the ability to generalize the results of antidepressant efficacy trials lacks empirical support, according to the authors.
In argumentation
In argumentation, the practice of "quote mining" is a form of cherry picking, in which the debater selectively picks some quotes supporting a position (or exaggerating an opposing position) while ignoring those that moderate the original quote or put it into a different context. Cherry picking in debates is a large problem as the facts themselves are true but need to be put in context. Because research cannot be done live and is often untimely, cherry-picked facts or quotes usually stick in the public mainstream and, even when corrected, lead to widespread misrepresentation of groups targeted.One-sided argument
A one-sided argument (also known as card stacking, stacking the deck, ignoring the counterevidence, slanting, and suppressed evidence) is an informal fallacy that occurs when only the reasons supporting a proposition are supplied, while all reasons opposing it are omitted. Philosophy professor Peter Suber has written: "The one-sidedness fallacy does not make an argument invalid. It may not even make the argument unsound. The fallacy consists in persuading readers, and perhaps ourselves, that we have said enough to tilt the scale of evidence and therefore enough to justify a judgment. If we have been one-sided, though, then we haven't yet said enough to justify a judgment. The arguments on the other side may be stronger than our own. We won't know until we examine them. So the one-sidedness fallacy doesn't mean that your premises are false or irrelevant, only that they are incomplete." "With rational messages, you need to decide if you want to use a one-sided argument or a two-sided argument. A one-sided argument presents only the pro side of the argument, while a two-sided argument presents both sides. Which one you use will depend on which one meets your needs and the type of audience. Generally, one-sided arguments are better with audiences already favorable to your message. Two-sided arguments are best with audiences who are opposed to your argument, are better educated or have already been exposed to counter arguments." Card stacking is a propaganda technique that seeks to manipulate audience perception of an issue by emphasizing one side and repressing another. Such emphasis may be achieved through media bias or the use of One-sided argument, one-sided testimonials, or by simply Censorship, censoring the voices of critics. The technique is commonly used in persuasive speeches by political candidates to discredit their opponents and to make themselves seem more worthy. The term originates from the Magic (illusion), magician's gimmick of "Glossary of poker terms#cold deck, stacking the deck", which involves presenting a Playing card, deck of cards that appears to have been randomly shuffled but which is, in fact, 'stacked' in a specific order. The magician knows the order and is able to control the outcome of the trick. In poker, cards can be stacked so that certain hands are dealt to certain players. The phenomenon can be applied to any subject and has wide applications. Whenever a broad spectrum of information exists, appearances can be rigged by highlighting some facts and ignoring others. Card stacking can be a tool of advocacy groups or of those groups with specific agendas. For example, an enlistment poster might focus upon an impressive picture, with words such as "travel" and "adventure", while placing the words, "enlist for two to four years" at the bottom in a smaller and less noticeable point size.See also
References
{{Propaganda Inductive fallacies Cognitive inertia Metaphors referring to food and drink Misuse of statistics Public relations techniques Evidence